-
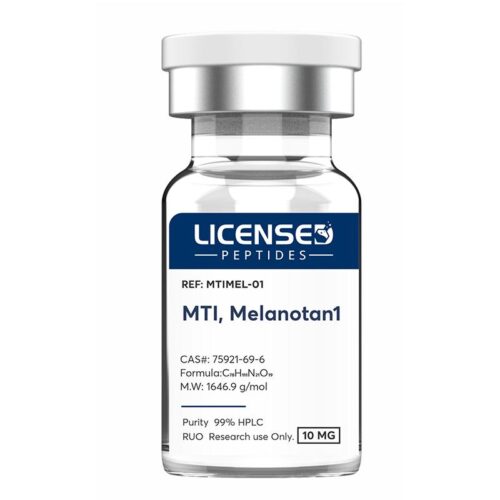
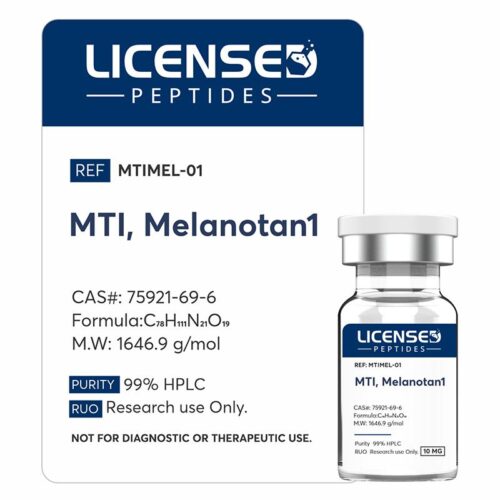 Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue closely related to the naturally occurring peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, also referred to as Melanotan 2). α-MSH plays a key role in regulating skin and hair pigmentation by acting on melanocytes through strong binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). As a non-selective full agonist, α-MSH also activates melanocortin receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Melanotan 1 differs from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution and was originally developed as a sunless tanning agent. Early studies confirmed its ability to induce pigmentation but also revealed broader effects, including changes in baseline metabolism. Research on Melanotan 1 and related melanocortin-binding peptides has since provided valuable insights into the melanocortin signaling system.
Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue closely related to the naturally occurring peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, also referred to as Melanotan 2). α-MSH plays a key role in regulating skin and hair pigmentation by acting on melanocytes through strong binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). As a non-selective full agonist, α-MSH also activates melanocortin receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Melanotan 1 differs from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution and was originally developed as a sunless tanning agent. Early studies confirmed its ability to induce pigmentation but also revealed broader effects, including changes in baseline metabolism. Research on Melanotan 1 and related melanocortin-binding peptides has since provided valuable insights into the melanocortin signaling system. -
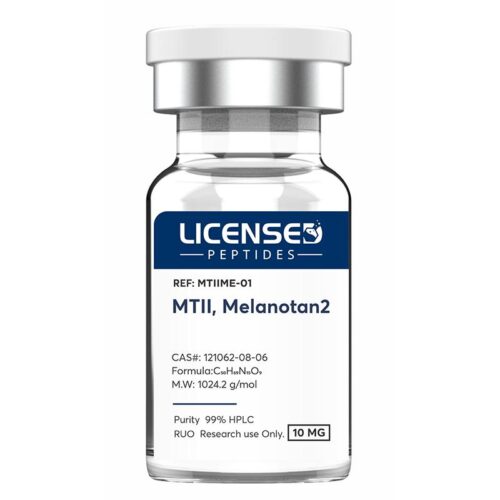
 Melanotan-2 (MT-2) is a synthetic analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), originally developed in the 1980s. Research indicates that MT-2 may influence several physiological processes, including enhancement of sexual arousal, reduction of compulsive or addictive behaviors, appetite suppression, and stimulation of melanin synthesis. By activating melanocytes, MT-2 promotes increased skin pigmentation. Preliminary studies have also suggested a potential role in supporting neurodevelopmental outcomes, with some evidence pointing to possible benefits in early interventions for autism.
Melanotan-2 (MT-2) is a synthetic analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), originally developed in the 1980s. Research indicates that MT-2 may influence several physiological processes, including enhancement of sexual arousal, reduction of compulsive or addictive behaviors, appetite suppression, and stimulation of melanin synthesis. By activating melanocytes, MT-2 promotes increased skin pigmentation. Preliminary studies have also suggested a potential role in supporting neurodevelopmental outcomes, with some evidence pointing to possible benefits in early interventions for autism. -

 PT-141, also known by its clinical name Bremelanotide, is a synthetic peptide derived from alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) through extensive structural modifications. It has undergone clinical evaluation for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in both men and women, as well as for applications in acute hemorrhagic conditions. PT-141 functions as an agonist at melanocortin-4 (MC4R) and melanocortin-1 (MC1R) receptors. Evidence from research indicates that it enhances sexual arousal and exerts immunomodulatory effects.
PT-141, also known by its clinical name Bremelanotide, is a synthetic peptide derived from alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) through extensive structural modifications. It has undergone clinical evaluation for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in both men and women, as well as for applications in acute hemorrhagic conditions. PT-141 functions as an agonist at melanocortin-4 (MC4R) and melanocortin-1 (MC1R) receptors. Evidence from research indicates that it enhances sexual arousal and exerts immunomodulatory effects. -

 Sermorelin is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) that is commonly used to evaluate and enhance endogenous growth hormone production. Research interest in sermorelin stems from its potential roles in promoting bone density, minimizing scar formation, mitigating cognitive decline associated with dementia, and reducing seizure occurrence.
Sermorelin is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) that is commonly used to evaluate and enhance endogenous growth hormone production. Research interest in sermorelin stems from its potential roles in promoting bone density, minimizing scar formation, mitigating cognitive decline associated with dementia, and reducing seizure occurrence. -

 MOTS-c is a 16–amino acid mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) that plays a key role in metabolic regulation. Produced within mitochondria, it helps maintain cellular energy balance by influencing glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and stress-response pathways. MOTS-c can translocate to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic adaptation, particularly during metabolic stress. Studies indicate that MOTS-c enhances exercise performance, reduces obesity and insulin resistance, and provides protective effects against conditions such as osteoporosis, metabolic disorders, and age-related diseases. In summary, MOTS-c supports metabolic homeostasis, healthy aging, and improved physical performance while mitigating the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and related disease states.
MOTS-c is a 16–amino acid mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) that plays a key role in metabolic regulation. Produced within mitochondria, it helps maintain cellular energy balance by influencing glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and stress-response pathways. MOTS-c can translocate to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic adaptation, particularly during metabolic stress. Studies indicate that MOTS-c enhances exercise performance, reduces obesity and insulin resistance, and provides protective effects against conditions such as osteoporosis, metabolic disorders, and age-related diseases. In summary, MOTS-c supports metabolic homeostasis, healthy aging, and improved physical performance while mitigating the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and related disease states. -

 Oxytocin is a peptide hormone with key physiological roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, maternal-infant bonding during lactation, and tissue repair. Beyond these established functions, emerging evidence indicates that oxytocin may enhance cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and mitigate complications associated with diabetes.
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone with key physiological roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, maternal-infant bonding during lactation, and tissue repair. Beyond these established functions, emerging evidence indicates that oxytocin may enhance cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and mitigate complications associated with diabetes. -
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -
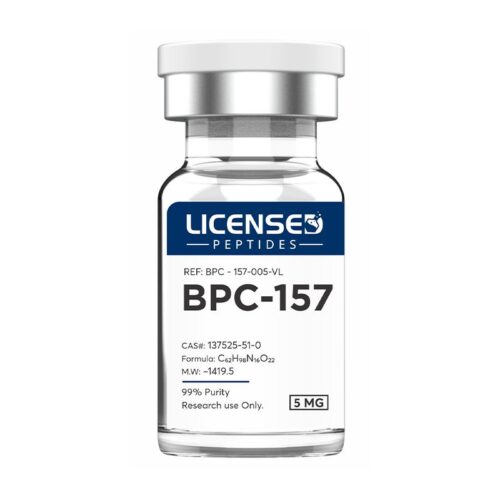
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -

 AOD9604 is a synthetic peptide fragment derived from human growth hormone (hGH), specifically from the 176-191 amino acid region of the hGH molecule. It was developed to mimic the fat-reducing (lipolytic) effects of hGH without the growth-promoting effects typically associated with the full hormone.
AOD9604 is a synthetic peptide fragment derived from human growth hormone (hGH), specifically from the 176-191 amino acid region of the hGH molecule. It was developed to mimic the fat-reducing (lipolytic) effects of hGH without the growth-promoting effects typically associated with the full hormone. -
 Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity.
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity. -
 Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline.
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline. -

 GHK-Cu is an endogenous peptide naturally present in human plasma, urine, and saliva. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that GHK-Cu enhances wound repair, supports immune function, and promotes skin regeneration by stimulating collagen synthesis, activating fibroblasts, and facilitating angiogenesis. Evidence also suggests that it functions as a feedback signal released following tissue injury. Additionally, GHK-Cu exhibits antioxidant properties by mitigating free radical–induced damage.
GHK-Cu is an endogenous peptide naturally present in human plasma, urine, and saliva. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that GHK-Cu enhances wound repair, supports immune function, and promotes skin regeneration by stimulating collagen synthesis, activating fibroblasts, and facilitating angiogenesis. Evidence also suggests that it functions as a feedback signal released following tissue injury. Additionally, GHK-Cu exhibits antioxidant properties by mitigating free radical–induced damage.
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you. +1 (570) 539-9711
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you.
+1 (570) 539-9711