-

 MOTS-c is a 16–amino acid mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) that plays a key role in metabolic regulation. Produced within mitochondria, it helps maintain cellular energy balance by influencing glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and stress-response pathways. MOTS-c can translocate to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic adaptation, particularly during metabolic stress. Studies indicate that MOTS-c enhances exercise performance, reduces obesity and insulin resistance, and provides protective effects against conditions such as osteoporosis, metabolic disorders, and age-related diseases. In summary, MOTS-c supports metabolic homeostasis, healthy aging, and improved physical performance while mitigating the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and related disease states.
MOTS-c is a 16–amino acid mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) that plays a key role in metabolic regulation. Produced within mitochondria, it helps maintain cellular energy balance by influencing glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and stress-response pathways. MOTS-c can translocate to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic adaptation, particularly during metabolic stress. Studies indicate that MOTS-c enhances exercise performance, reduces obesity and insulin resistance, and provides protective effects against conditions such as osteoporosis, metabolic disorders, and age-related diseases. In summary, MOTS-c supports metabolic homeostasis, healthy aging, and improved physical performance while mitigating the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and related disease states. -
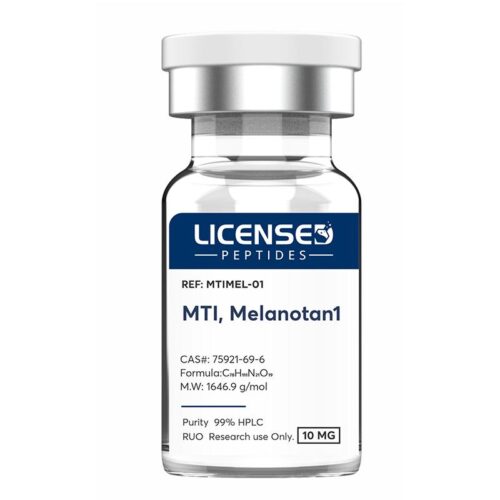
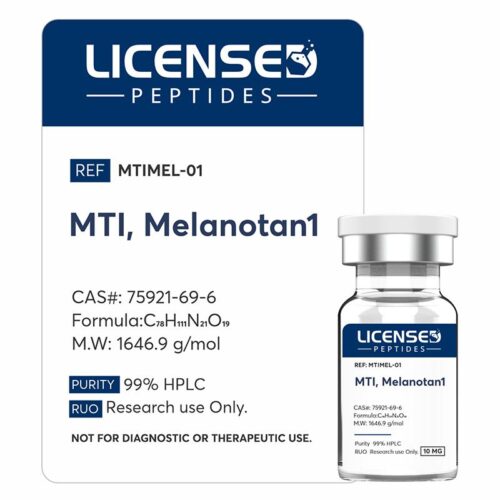 Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue closely related to the naturally occurring peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, also referred to as Melanotan 2). α-MSH plays a key role in regulating skin and hair pigmentation by acting on melanocytes through strong binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). As a non-selective full agonist, α-MSH also activates melanocortin receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Melanotan 1 differs from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution and was originally developed as a sunless tanning agent. Early studies confirmed its ability to induce pigmentation but also revealed broader effects, including changes in baseline metabolism. Research on Melanotan 1 and related melanocortin-binding peptides has since provided valuable insights into the melanocortin signaling system.
Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue closely related to the naturally occurring peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, also referred to as Melanotan 2). α-MSH plays a key role in regulating skin and hair pigmentation by acting on melanocytes through strong binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). As a non-selective full agonist, α-MSH also activates melanocortin receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Melanotan 1 differs from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution and was originally developed as a sunless tanning agent. Early studies confirmed its ability to induce pigmentation but also revealed broader effects, including changes in baseline metabolism. Research on Melanotan 1 and related melanocortin-binding peptides has since provided valuable insights into the melanocortin signaling system. -
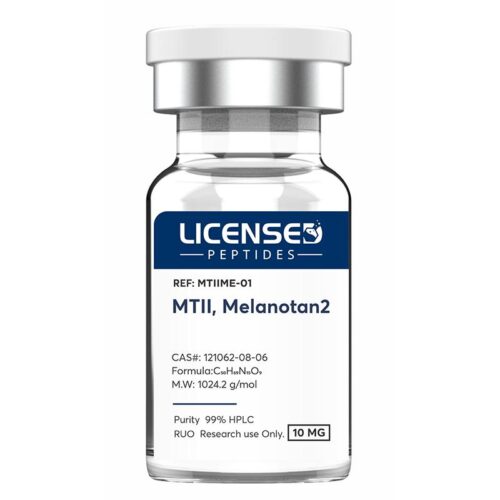
 Melanotan-2 (MT-2) is a synthetic analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), originally developed in the 1980s. Research indicates that MT-2 may influence several physiological processes, including enhancement of sexual arousal, reduction of compulsive or addictive behaviors, appetite suppression, and stimulation of melanin synthesis. By activating melanocytes, MT-2 promotes increased skin pigmentation. Preliminary studies have also suggested a potential role in supporting neurodevelopmental outcomes, with some evidence pointing to possible benefits in early interventions for autism.
Melanotan-2 (MT-2) is a synthetic analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), originally developed in the 1980s. Research indicates that MT-2 may influence several physiological processes, including enhancement of sexual arousal, reduction of compulsive or addictive behaviors, appetite suppression, and stimulation of melanin synthesis. By activating melanocytes, MT-2 promotes increased skin pigmentation. Preliminary studies have also suggested a potential role in supporting neurodevelopmental outcomes, with some evidence pointing to possible benefits in early interventions for autism. -

 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential pyridine nucleotide and ubiquitous coenzyme present in all living cells, where it plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Acting as a redox mediator, NAD+ undergoes continuous interconversion between its oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) states, thereby facilitating electron transfer reactions fundamental to oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. Beyond its canonical role in energy metabolism, NAD+ serves as a critical co-substrate in more than 500 enzymatic reactions, underscoring its broad involvement in cellular homeostasis. Accumulating evidence suggests that maintenance of NAD+ levels contributes to enhanced skeletal muscle function, neuroprotection, and attenuation of age-associated physiological decline.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential pyridine nucleotide and ubiquitous coenzyme present in all living cells, where it plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Acting as a redox mediator, NAD+ undergoes continuous interconversion between its oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) states, thereby facilitating electron transfer reactions fundamental to oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. Beyond its canonical role in energy metabolism, NAD+ serves as a critical co-substrate in more than 500 enzymatic reactions, underscoring its broad involvement in cellular homeostasis. Accumulating evidence suggests that maintenance of NAD+ levels contributes to enhanced skeletal muscle function, neuroprotection, and attenuation of age-associated physiological decline. -

 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential pyridine nucleotide and ubiquitous coenzyme present in all living cells, where it plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Acting as a redox mediator, NAD+ undergoes continuous interconversion between its oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) states, thereby facilitating electron transfer reactions fundamental to oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. Beyond its canonical role in energy metabolism, NAD+ serves as a critical co-substrate in more than 500 enzymatic reactions, underscoring its broad involvement in cellular homeostasis. Accumulating evidence suggests that maintenance of NAD+ levels contributes to enhanced skeletal muscle function, neuroprotection, and attenuation of age-associated physiological decline.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential pyridine nucleotide and ubiquitous coenzyme present in all living cells, where it plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Acting as a redox mediator, NAD+ undergoes continuous interconversion between its oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) states, thereby facilitating electron transfer reactions fundamental to oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. Beyond its canonical role in energy metabolism, NAD+ serves as a critical co-substrate in more than 500 enzymatic reactions, underscoring its broad involvement in cellular homeostasis. Accumulating evidence suggests that maintenance of NAD+ levels contributes to enhanced skeletal muscle function, neuroprotection, and attenuation of age-associated physiological decline. -

 Oxytocin is a peptide hormone with key physiological roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, maternal-infant bonding during lactation, and tissue repair. Beyond these established functions, emerging evidence indicates that oxytocin may enhance cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and mitigate complications associated with diabetes.
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone with key physiological roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, maternal-infant bonding during lactation, and tissue repair. Beyond these established functions, emerging evidence indicates that oxytocin may enhance cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and mitigate complications associated with diabetes. -

 PT-141, also known by its clinical name Bremelanotide, is a synthetic peptide derived from alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) through extensive structural modifications. It has undergone clinical evaluation for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in both men and women, as well as for applications in acute hemorrhagic conditions. PT-141 functions as an agonist at melanocortin-4 (MC4R) and melanocortin-1 (MC1R) receptors. Evidence from research indicates that it enhances sexual arousal and exerts immunomodulatory effects.
PT-141, also known by its clinical name Bremelanotide, is a synthetic peptide derived from alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) through extensive structural modifications. It has undergone clinical evaluation for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in both men and women, as well as for applications in acute hemorrhagic conditions. PT-141 functions as an agonist at melanocortin-4 (MC4R) and melanocortin-1 (MC1R) receptors. Evidence from research indicates that it enhances sexual arousal and exerts immunomodulatory effects. -

 Sermorelin is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) that is commonly used to evaluate and enhance endogenous growth hormone production. Research interest in sermorelin stems from its potential roles in promoting bone density, minimizing scar formation, mitigating cognitive decline associated with dementia, and reducing seizure occurrence.
Sermorelin is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) that is commonly used to evaluate and enhance endogenous growth hormone production. Research interest in sermorelin stems from its potential roles in promoting bone density, minimizing scar formation, mitigating cognitive decline associated with dementia, and reducing seizure occurrence. -

 SLU-PP-332 is an investigational compound under study for its ability to reproduce some of the physiological effects typically associated with exercise. Its mechanism of action involves activation of estrogen-related receptors (ERRα, ERRβ, and ERRγ), which are central regulators of energy metabolism. Through this pathway, the compound has been shown to enhance mitochondrial efficiency, increase fatty acid oxidation, and elevate overall energy expenditure. In preclinical studies involving both diet-induced and genetically obese mice, administration of SLU-PP-332 produced significant metabolic improvements. Animals receiving the compound demonstrated reduced fat mass and greater rates of fatty acid utilization, while food intake and physical activity remained unchanged. These findings suggest that the compound alters systemic energy balance, creating a more favorable metabolic profile without requiring lifestyle modification. Additional investigations have highlighted the compound’s effects on skeletal muscle physiology. Treatment was associated with a higher proportion of oxidative muscle fibers, a shift that supports endurance capacity. Functional outcomes reflected this change, as mice receiving SLU-PP-332 exhibited prolonged exercise tolerance. Mechanistic studies attributed these effects to enhanced mitochondrial respiration and improved cellular bioenergetics within muscle tissue.
SLU-PP-332 is an investigational compound under study for its ability to reproduce some of the physiological effects typically associated with exercise. Its mechanism of action involves activation of estrogen-related receptors (ERRα, ERRβ, and ERRγ), which are central regulators of energy metabolism. Through this pathway, the compound has been shown to enhance mitochondrial efficiency, increase fatty acid oxidation, and elevate overall energy expenditure. In preclinical studies involving both diet-induced and genetically obese mice, administration of SLU-PP-332 produced significant metabolic improvements. Animals receiving the compound demonstrated reduced fat mass and greater rates of fatty acid utilization, while food intake and physical activity remained unchanged. These findings suggest that the compound alters systemic energy balance, creating a more favorable metabolic profile without requiring lifestyle modification. Additional investigations have highlighted the compound’s effects on skeletal muscle physiology. Treatment was associated with a higher proportion of oxidative muscle fibers, a shift that supports endurance capacity. Functional outcomes reflected this change, as mice receiving SLU-PP-332 exhibited prolonged exercise tolerance. Mechanistic studies attributed these effects to enhanced mitochondrial respiration and improved cellular bioenergetics within muscle tissue. -
 TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) is a synthetic peptide consisting of 43 amino acids. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that Thymosin Beta-4 supports angiogenesis, modulates wound healing, reduces inflammation, and mitigates oxidative stress in both cardiac and neurological tissues. It plays a critical role in cytoprotection, tissue repair, regeneration, and structural remodeling following injury. Due to these properties, it has also attracted significant interest within the field of anti-aging research.
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) is a synthetic peptide consisting of 43 amino acids. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that Thymosin Beta-4 supports angiogenesis, modulates wound healing, reduces inflammation, and mitigates oxidative stress in both cardiac and neurological tissues. It plays a critical role in cytoprotection, tissue repair, regeneration, and structural remodeling following injury. Due to these properties, it has also attracted significant interest within the field of anti-aging research. -

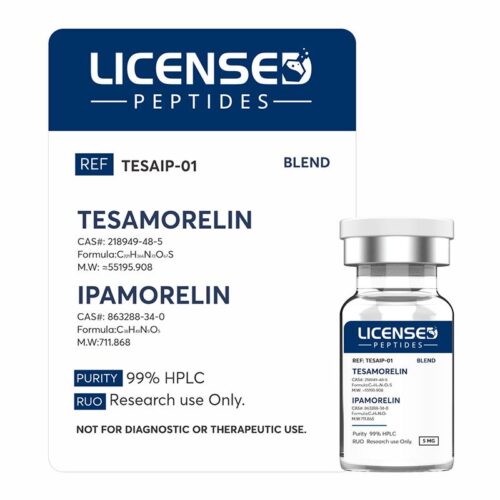
 Tesamorelin is a synthetic peptide analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), composed of 44 amino acids with a structural modification that enhances its stability and half-life. Although it has gained regulatory approval as Egrifta® for the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy, tesamorelin is also widely investigated in the broader research context.
Tesamorelin is a synthetic peptide analogue of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), composed of 44 amino acids with a structural modification that enhances its stability and half-life. Although it has gained regulatory approval as Egrifta® for the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy, tesamorelin is also widely investigated in the broader research context.
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you. +1 (570) 539-9711
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you.
+1 (570) 539-9711