-

 5-amino-1MQ is a small molecule that inhibits the enzyme nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), which plays a key role in metabolism and energy regulation, particularly in fat tissue. By blocking NNMT, 5-amino-1MQ increases levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a critical cofactor in cellular metabolism. This increase in NAD⁺ enhances metabolic activity and activates the SIRT1 gene, also known as the “longevity gene.” SIRT1 is associated with a reduced risk of various chronic conditions, including diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, kidney and liver disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers. In studies involving mice, treatment with 5-amino-1MQ led to a 7% reduction in body mass within 10 days, without any change in food consumption compared to untreated controls. Additional research suggests that lowering NNMT activity may help shrink fat cells and decrease fat accumulation.
5-amino-1MQ is a small molecule that inhibits the enzyme nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), which plays a key role in metabolism and energy regulation, particularly in fat tissue. By blocking NNMT, 5-amino-1MQ increases levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a critical cofactor in cellular metabolism. This increase in NAD⁺ enhances metabolic activity and activates the SIRT1 gene, also known as the “longevity gene.” SIRT1 is associated with a reduced risk of various chronic conditions, including diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, kidney and liver disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers. In studies involving mice, treatment with 5-amino-1MQ led to a 7% reduction in body mass within 10 days, without any change in food consumption compared to untreated controls. Additional research suggests that lowering NNMT activity may help shrink fat cells and decrease fat accumulation. -

 AOD9604 is a synthetic peptide fragment derived from human growth hormone (hGH), specifically from the 176-191 amino acid region of the hGH molecule. It was developed to mimic the fat-reducing (lipolytic) effects of hGH without the growth-promoting effects typically associated with the full hormone.
AOD9604 is a synthetic peptide fragment derived from human growth hormone (hGH), specifically from the 176-191 amino acid region of the hGH molecule. It was developed to mimic the fat-reducing (lipolytic) effects of hGH without the growth-promoting effects typically associated with the full hormone. -
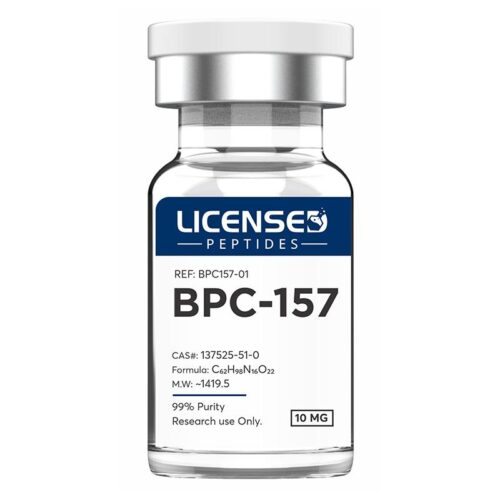
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -
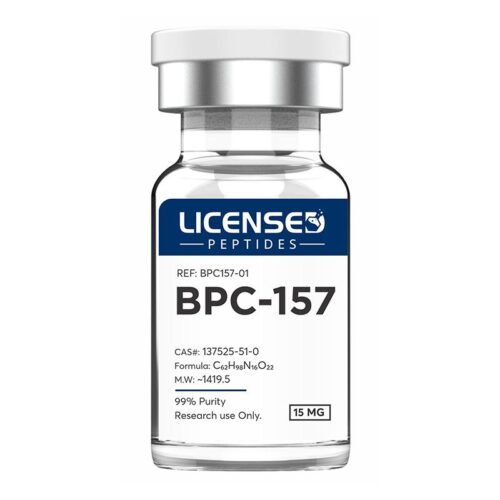
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -
 BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support.
BPC-157 is a peptide made up of 15 amino acids, originally discovered in human gastric juice. Research shows that it supports faster healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even skin injuries such as burns. It also helps protect organs and may prevent gastric ulcers. In the digestive system, BPC-157 has been shown to support gut health by helping with issues like leaky gut, IBS, cramps, and Crohn’s disease. In addition, it may reduce pain and speed up recovery by improving blood flow, boosting collagen production, and supporting new tissue and blood vessel growth. Because of these benefits, BPC-157 is being studied as a promising option for wound healing and overall recovery support. -
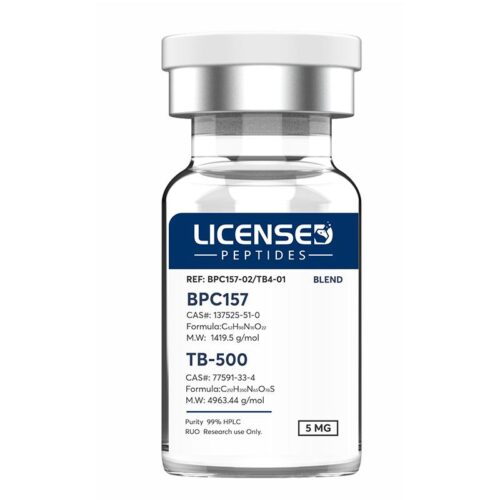
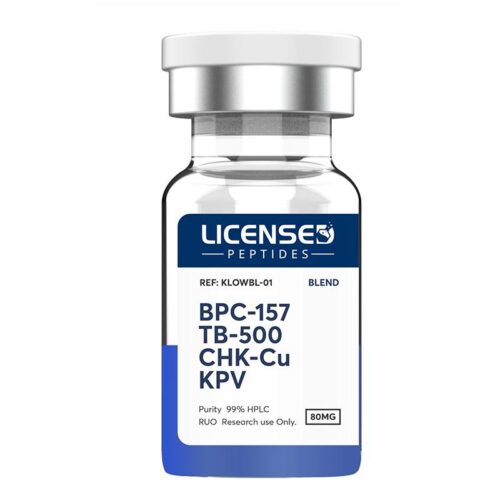
 BPC-157: A stable pentadecapeptide originally isolated from gastric juice, BPC-157 is recognized for its ability to stimulate new blood vessel formation, encourage fibroblast migration, and support epithelial repair. These effects are thought to involve modulation of VEGFR2 activity, FAK-paxillin signaling, and nitric oxide pathways. Preclinical studies suggest it promotes the healing of tendons, muscle tissue, and the gastrointestinal tract. TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4 fragment): This 43-amino acid peptide regulates actin dynamics, facilitating cellular movement and tissue regeneration. It enhances repair processes by promoting angiogenesis (partly through VEGF upregulation), reducing inflammation, and mobilizing progenitor cells. Evidence indicates it may accelerate recovery in cardiac tissue, dermal layers, and connective structures. GHK-Cu: A naturally occurring copper-binding tripeptide (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) with broad regenerative activity. It has been shown to encourage wound repair, stimulate collagen and extracellular matrix production, and support hair growth. Mechanistically, it influences gene networks involved in tissue remodeling and exerts protective antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions, partly through TGF-β signaling and regulation of metalloproteinases.
BPC-157: A stable pentadecapeptide originally isolated from gastric juice, BPC-157 is recognized for its ability to stimulate new blood vessel formation, encourage fibroblast migration, and support epithelial repair. These effects are thought to involve modulation of VEGFR2 activity, FAK-paxillin signaling, and nitric oxide pathways. Preclinical studies suggest it promotes the healing of tendons, muscle tissue, and the gastrointestinal tract. TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4 fragment): This 43-amino acid peptide regulates actin dynamics, facilitating cellular movement and tissue regeneration. It enhances repair processes by promoting angiogenesis (partly through VEGF upregulation), reducing inflammation, and mobilizing progenitor cells. Evidence indicates it may accelerate recovery in cardiac tissue, dermal layers, and connective structures. GHK-Cu: A naturally occurring copper-binding tripeptide (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) with broad regenerative activity. It has been shown to encourage wound repair, stimulate collagen and extracellular matrix production, and support hair growth. Mechanistically, it influences gene networks involved in tissue remodeling and exerts protective antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions, partly through TGF-β signaling and regulation of metalloproteinases. -

 Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a natural peptide released alongside insulin. In animal studies, it has shown potential for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these uses, research has explored its possible benefits for liver injury, alcohol-related liver disease, and cardiovascular conditions. There is also speculation about its role in Alzheimer’s disease, though no studies have yet been published in that area. Several trials have examined cagrilintide in combination with semaglutide for obesity and type 2 diabetes, with evidence suggesting the two agents may act synergistically to promote greater and more sustained weight loss. While preclinical findings are encouraging, clinical data in humans remain limited, and further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety.
Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a natural peptide released alongside insulin. In animal studies, it has shown potential for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these uses, research has explored its possible benefits for liver injury, alcohol-related liver disease, and cardiovascular conditions. There is also speculation about its role in Alzheimer’s disease, though no studies have yet been published in that area. Several trials have examined cagrilintide in combination with semaglutide for obesity and type 2 diabetes, with evidence suggesting the two agents may act synergistically to promote greater and more sustained weight loss. While preclinical findings are encouraging, clinical data in humans remain limited, and further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety. -

 Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a natural peptide released alongside insulin. In animal studies, it has shown potential for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these uses, research has explored its possible benefits for liver injury, alcohol-related liver disease, and cardiovascular conditions. There is also speculation about its role in Alzheimer’s disease, though no studies have yet been published in that area. Several trials have examined cagrilintide in combination with semaglutide for obesity and type 2 diabetes, with evidence suggesting the two agents may act synergistically to promote greater and more sustained weight loss. While preclinical findings are encouraging, clinical data in humans remain limited, and further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety.
Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a natural peptide released alongside insulin. In animal studies, it has shown potential for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these uses, research has explored its possible benefits for liver injury, alcohol-related liver disease, and cardiovascular conditions. There is also speculation about its role in Alzheimer’s disease, though no studies have yet been published in that area. Several trials have examined cagrilintide in combination with semaglutide for obesity and type 2 diabetes, with evidence suggesting the two agents may act synergistically to promote greater and more sustained weight loss. While preclinical findings are encouraging, clinical data in humans remain limited, and further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety. -

 CJC-1295 supports the body’s own production of growth hormone (GH) by activating the growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) receptor. Ipamorelin is considered one of the most selective GH secretagogues and functions as a strong agonist of the ghrelin/GH secretagogue receptor. Research has investigated its potential in several areas, indicating benefits such as enhanced bone strength, accelerated muscle repair and growth, stimulation of pancreatic insulin release, and support for gastrointestinal activity and motility. When studied in combination, CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin have demonstrated complementary and synergistic effects on GH release.
CJC-1295 supports the body’s own production of growth hormone (GH) by activating the growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) receptor. Ipamorelin is considered one of the most selective GH secretagogues and functions as a strong agonist of the ghrelin/GH secretagogue receptor. Research has investigated its potential in several areas, indicating benefits such as enhanced bone strength, accelerated muscle repair and growth, stimulation of pancreatic insulin release, and support for gastrointestinal activity and motility. When studied in combination, CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin have demonstrated complementary and synergistic effects on GH release. -

 CJC-1295 DAC is a synthetic peptide designed as an analog of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH). Its primary purpose is to stimulate the pituitary gland to release more growth hormone, which subsequently elevates levels of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1). What sets the DAC version apart from the non-DAC form is the addition of a “Drug Affinity Complex.” This chemical modification allows CJC-1295 DAC to bind to albumin in the bloodstream, extending its half-life from just minutes to several days. Because of this extended duration, a single administration can keep growth hormone levels elevated for nearly a week, making it significantly more efficient in terms of dosing frequency compared to its short-lived counterpart. In research contexts, CJC-1295 DAC has been studied for its potential to promote tissue repair, support lean muscle growth, improve fat metabolism, enhance sleep quality, and contribute to overall cellular rejuvenation. These effects are largely connected to the consistent elevation of growth hormone and IGF-1, which play central roles in recovery, metabolism, and anti-aging pathways. Despite these promising avenues, CJC-1295 DAC remains a research chemical rather than an approved therapeutic drug. Human studies are limited, and while side effects observed have included injection site reactions, water retention, flushing, and tingling, the long-term implications are not yet fully understood. Because of this, its use outside of supervised research carries risks, and it is not approved by regulatory authorities for medical treatment.
CJC-1295 DAC is a synthetic peptide designed as an analog of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH). Its primary purpose is to stimulate the pituitary gland to release more growth hormone, which subsequently elevates levels of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1). What sets the DAC version apart from the non-DAC form is the addition of a “Drug Affinity Complex.” This chemical modification allows CJC-1295 DAC to bind to albumin in the bloodstream, extending its half-life from just minutes to several days. Because of this extended duration, a single administration can keep growth hormone levels elevated for nearly a week, making it significantly more efficient in terms of dosing frequency compared to its short-lived counterpart. In research contexts, CJC-1295 DAC has been studied for its potential to promote tissue repair, support lean muscle growth, improve fat metabolism, enhance sleep quality, and contribute to overall cellular rejuvenation. These effects are largely connected to the consistent elevation of growth hormone and IGF-1, which play central roles in recovery, metabolism, and anti-aging pathways. Despite these promising avenues, CJC-1295 DAC remains a research chemical rather than an approved therapeutic drug. Human studies are limited, and while side effects observed have included injection site reactions, water retention, flushing, and tingling, the long-term implications are not yet fully understood. Because of this, its use outside of supervised research carries risks, and it is not approved by regulatory authorities for medical treatment. -

 CJC-1295 No DAC (Modified GRF) is a shortened peptide derivative of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH). Originally developed in the 1980s, studies on modGRF suggest it may support muscle repair and development, speed up wound recovery, enhance bone strength, boost fat metabolism, and promote overall metabolic health. Research also indicates it could play a role in regulating blood sugar levels and supporting immune function.
CJC-1295 No DAC (Modified GRF) is a shortened peptide derivative of growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH). Originally developed in the 1980s, studies on modGRF suggest it may support muscle repair and development, speed up wound recovery, enhance bone strength, boost fat metabolism, and promote overall metabolic health. Research also indicates it could play a role in regulating blood sugar levels and supporting immune function. -
 Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline.
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline. -

 Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline.
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline. -

 Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline.
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline. -

 GHK-Cu is an endogenous peptide naturally present in human plasma, urine, and saliva. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that GHK-Cu enhances wound repair, supports immune function, and promotes skin regeneration by stimulating collagen synthesis, activating fibroblasts, and facilitating angiogenesis. Evidence also suggests that it functions as a feedback signal released following tissue injury. Additionally, GHK-Cu exhibits antioxidant properties by mitigating free radical–induced damage.
GHK-Cu is an endogenous peptide naturally present in human plasma, urine, and saliva. Preclinical studies in animal models indicate that GHK-Cu enhances wound repair, supports immune function, and promotes skin regeneration by stimulating collagen synthesis, activating fibroblasts, and facilitating angiogenesis. Evidence also suggests that it functions as a feedback signal released following tissue injury. Additionally, GHK-Cu exhibits antioxidant properties by mitigating free radical–induced damage. -

 Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity.
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity. -
 Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity.
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity. -
 Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity.
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016). Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021). Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity. -

 Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways.
Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways. -
 Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways.
Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways. -
 Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways.
Tirzepatide is a dual agonist targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors—novel dual incretin-based therapy. Its design integrates both GLP-1 and GIP actions in a single molecule, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety through central nervous system pathways.
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you. +1 (570) 539-9711
Need help? Call Or Text us, and a team member will be happy to assist you.
+1 (570) 539-9711