Cagrilintide 10mg
$154.99
Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a natural peptide released alongside insulin. In animal studies, it has shown potential for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these uses, research has explored its possible benefits for liver injury, alcohol-related liver disease, and cardiovascular conditions. There is also speculation about its role in Alzheimer’s disease, though no studies have yet been published in that area. Several trials have examined cagrilintide in combination with semaglutide for obesity and type 2 diabetes, with evidence suggesting the two agents may act synergistically to promote greater and more sustained weight loss. While preclinical findings are encouraging, clinical data in humans remain limited, and further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety.
$154.99
$154.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Cagrilintide Overview:
Cagrilintide is a long-acting analogue of amylin, a hormone that is naturally secreted alongside insulin. It has demonstrated potential in preclinical and clinical studies as a therapy for obesity and type 2 diabetes. Beyond these conditions, cagrilintide has been explored for its possible benefits in liver disease (including alcohol-related liver damage), as well as cardiovascular disorders. There has also been early speculation about a role in Alzheimer’s disease, although no published studies have yet confirmed this.
Much of the current research has focused on combining cagrilintide with semaglutide for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. This combination appears to act synergistically, producing greater and more sustained weight loss compared to either agent alone.
Cagrilintide: Structure
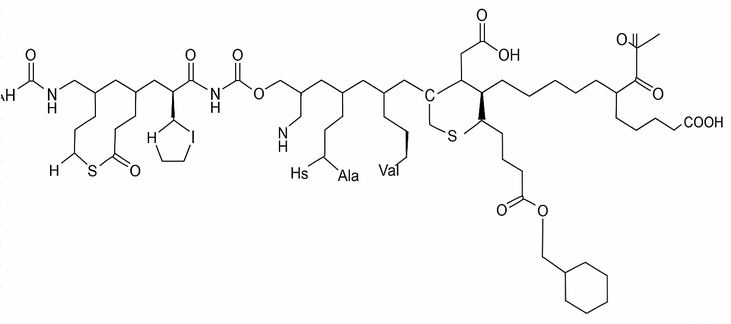
Molecular formula: C₁₉₁H₂₉₄N₅₂O₅₈S₂
Molecular weight: ~ 4226.8 g/mol
Peptide length: 37 amino acids
Disulfide bonds: 1 (between Cys² and Cys⁷)
Modification: Lipidation at Lys²⁸ via γ-glutamic acid linker and C16 fatty diacid
Type: Long-acting amylin analogue (peptide drug)
Half-life: ~8 days (due to lipidation and albumin binding)
Source: PubChem
Cagrilintide: Research
What is Cagrilintide?
Obesity and type 2 diabetes are chronic, relapsing conditions that impose a major global health burden. Despite the success of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), many patients fail to achieve or sustain sufficient weight reduction with current therapies. Amylin, a peptide hormone co-secreted with insulin, has long been recognized as a target for weight and glycemic control due to its role in regulating satiety, gastric emptying, and postprandial glucagon secretion. However, the native hormone is unstable and prone to aggregation, limiting its therapeutic use.
Cagrilintide (NNC0174-0833) is a long-acting, acylated amylin analogue developed by Novo Nordisk. By combining the physiological actions of amylin with structural modifications that enhance stability and extend half-life, cagrilintide represents a new therapeutic approach for chronic weight management and type 2 diabetes.
Mechanism of Action
Cagrilintide is a 37–amino acid peptide structurally related to human amylin, modified with a C16 fatty diacid side chain linked via a γ-glutamic acid spacer at Lys²⁸. This lipidation promotes albumin binding, extending its plasma half-life to approximately one week, which allows for once-weekly dosing.
At the receptor level, cagrilintide activates amylin receptors, which are heterodimers consisting of the calcitonin receptor (CTR) combined with receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs). Preclinical work has shown that cagrilintide’s weight-lowering effects are mediated primarily via AMY1 and AMY3 receptor subtypes, which are highly expressed in appetite-regulating regions of the brain. This results in reduced food intake, delayed gastric emptying, and improved satiety. Importantly, its mechanism is complementary to GLP-1 receptor agonists, making it an attractive candidate for combination therapy.
Clinical Development in Obesity
Phase 2 Studies
In a pivotal Phase 2 trial (Lancet 2021), adults with overweight or obesity were randomized to receive weekly injections of cagrilintide, liraglutide, or placebo for up to 68 weeks. Results demonstrated dose-dependent weight loss, with cagrilintide producing clinically meaningful reductions in body weight compared to placebo and, at certain doses, exceeding those achieved with liraglutide. The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting), which were generally mild to moderate.
Phase 3 Studies
The REDEFINE-1 trial (NEJM 2025) investigated the fixed-dose combination of cagrilintide (2.4 mg) with semaglutide (2.4 mg), branded in development as CagriSema, in adults with obesity but without diabetes. After 68 weeks, participants in the combination group achieved an impressive 22.7% mean body-weight reduction (20.4% in the ITT analysis), compared to ~2–3% with placebo. A substantial proportion of participants achieved ≥20% or even ≥25% weight loss, magnitudes approaching those observed with bariatric surgery. Gastrointestinal events were the most frequent side effects, but overall tolerability was consistent with other incretin-based therapies.
Clinical Development in Type 2 Diabetes
Phase 2 Studies
A Phase 2 trial (Lancet 2023) assessed the combination of cagrilintide and semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes. The combination produced greater reductions in body weight and HbA1c compared to either agent alone or placebo, confirming the complementary nature of amylin and GLP-1 pathways.
Phase 3 Studies
The REDEFINE-2 trial (NEJM 2025) extended these findings to a larger cohort of adults with type 2 diabetes and obesity. After 68 weeks, CagriSema achieved average weight losses of 15–16% alongside clinically significant HbA1c reductions compared to placebo. Safety was dominated by gastrointestinal side effects during titration but was otherwise favorable, with no unexpected safety signals.
Summary
Cagrilintide is a next-generation, long-acting amylin analogue that represents a new therapeutic class in obesity and diabetes care. As monotherapy, it produces meaningful weight loss; when combined with semaglutide, the effects are among the strongest seen with injectable therapies, reaching weight-loss magnitudes previously associated with bariatric surgery. Its complementary mechanism and once-weekly dosing make it a promising candidate for long-term treatment of obesity, with or without type 2 diabetes.
Cagrilintide : Scientific Journal & Authors
Dr. Thomas Lutz studied veterinary medicine at the University of Berlin, FRG, and did his veterinary doctoral thesis at the University of Zurich on epithelial electrolyte transport. He completed a PhD at the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, on the pathophysiology of feline diabetes mellitus. He became Professor in Veterinary Physiology at the University of Zurich in 2004. His research focuses on the neuroendocrine control of eating, the pathophysiology of obesity and on the pathophysiology of obesity-related comorbidities like type 2 diabetes mellitus. Linked to that is a specific focus on weight lowering therapy and multi-organ crosstalk.
Dr. Thomas Lutz is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of Cagrilintide. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. The purpose of citing the doctor is to acknowledge, recognize, and credit the exhaustive research and development efforts conducted by the scientists studying this peptide.
Referenced Citations
Kruse T, Christoffersen BØ, Mortensen K, et al. Design and pharmacological characterization of cagrilintide (NNC0174-0833)… Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021; 64(12):8942–8954. [View on Journal of Med Chem] (Exact URL not available through search result)
T.A Lutz, “Creating the Amylin Story”
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below:




