Epithalon 20mg
$89.99
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) originally developed as an analogue of the naturally occurring pineal peptide complex, Epithalamin. It has been proposed to act as a modulator of telomerase activity, the ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex responsible for the preservation and elongation of telomeric DNA sequences at chromosomal termini. Experimental evidence suggests that Epithalon may facilitate telomere extension, thereby enhancing genomic stability, delaying replicative senescence, and exerting potential geroprotective effects through the attenuation of age-associated cellular decline.
$89.99
$89.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Overview
Epithalon (also referred to as Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide with the amino acid sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly. It was developed as an analogue of Epithalamin, a peptide complex naturally secreted by the pineal gland.
In research contexts, Epithalon is primarily studied for its role as a potential modulator of telomerase, the enzyme that maintains telomere length at the ends of chromosomes. By influencing telomerase activity, Epithalon has been shown in experimental models to promote telomere elongation, which may contribute to enhanced genomic stability, delayed cellular senescence, and possible anti-aging (geroprotective) effects.
Additional investigations have explored its roles in:
- Antioxidant regulation (reducing oxidative stress)
- Immunomodulation (supporting immune function).
- Oncological research, given telomerase involvement in cancer biology.
Epithalon : Structure
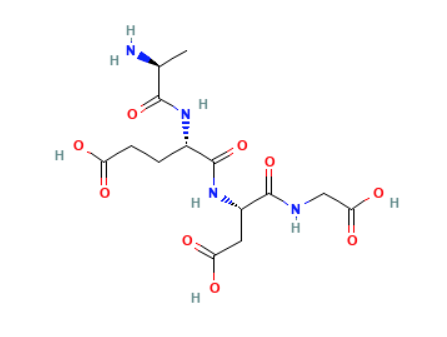
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₂N₄O₉
Molecular Weight: 390.349 g/mol
PubChem CID: 219042
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Source: PubChem
Epithalon : Research
Aging & Mortality Reduction
In elderly individuals, Epithalamin (the natural extract counterpart) reduced all-cause and cardiovascular mortality by 28%, improved cardiovascular health and exercise tolerance in a 12-year randomized clinical trial.
Epithalon and Skin Health
Epithalon has been shown to exert regulatory effects on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), an enzyme critically involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling within connective tissues, including the skin. Preclinical investigations in rodent models demonstrate that Epithalon not only upregulates MMP-2 gene expression but also stimulates the activity of fibroblasts the principal cells responsible for the synthesis and maintenance of ECM components such as collagen and elastin. Experimental data indicate that exposure to Epithalon increases fibroblast activation by approximately 30–45%, thereby enhancing reparative capacity and counteracting age-related deterioration in dermal architecture and integrity.
Additional mechanistic insights highlight Epithalon’s role in modulating caspase-3 activity, a key effector enzyme in the apoptotic signaling cascade. By attenuating caspase-3 activity, Epithalon confers protective effects on fibroblasts and other cutaneous cell populations, prolonging cellular viability and functional capacity. Collectively, these findings suggest that Epithalon contributes to the preservation of skin structure and function through coordinated regulation of ECM homeostasis and apoptosis-associated pathways.
Epithalon and Melatonin Secretion
Melatonin, a neurohormone produced by the pineal gland, plays a central role in regulating circadian rhythms and has been closely associated with both sleep regulation and aging processes. Experimental studies in rodents have demonstrated that Epithalon, along with related peptide analogues, modulates melatonin synthesis and secretion through the regulation of gene expression. Specifically, Epithalon influences the activity of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) and phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein (pCREB)—two key regulatory proteins essential for melatonin biosynthesis and circadian control of its release.
Moreover, primate studies provide evidence that Epithalon administration restores melatonin secretion to physiological levels, suggesting a potential role in re-establishing circadian homeostasis and counteracting age-associated declines in pineal function.
Epithalon : Scientific Journal & Authors
Vladimir Khavinson is a Professor and leading gerontologist, serving as President of the European region of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics and member of the Russian and Ukrainian Academies of Medical Sciences. He is Director of the Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology and has focused his career on the study of peptides in aging and longevity.
Khavinson is recognized for developing peptide-based bioregulators and geroprotectors, with over 196 patents, 775 scientific publications, and numerous clinical applications, including six pharmaceuticals and 64 peptide-based supplements. His research emphasizes peptide therapies for slowing aging, extending lifespan, and maintaining health.
Referenced Citations
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below: