GLP1-S 20mg
$179.99
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. As an analogue of endogenous GLP-1, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and promote satiety, thereby improving glycemic control and reducing body weight (Nauck & Meier, 2019). Its molecular modifications, including substitution of alanine at position 8 and attachment of a C18 fatty diacid chain, extend its half-life to approximately one week, enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016).
Semaglutide was initially approved for the management of type 2 diabetes under the trade name Ozempic and later for chronic weight management under the brand Wegovy. Large-scale clinical trials, such as the SUSTAIN and STEP programs, demonstrated significant reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), meaningful weight loss, and favorable cardiovascular outcomes in patients at high risk (Wilding et al., 2021; Marso et al., 2016). Beyond diabetes and obesity, ongoing research is evaluating semaglutide’s potential role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders (Newsome et al., 2021).
Given its robust clinical efficacy and broad therapeutic potential, semaglutide represents a major advancement in metabolic medicine and has reshaped the treatment paradigm for both diabetes and obesity.
$179.99
$179.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) that has emerged as a cornerstone therapy in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. GLP-1 is an incretin hormone secreted by intestinal L-cells in response to nutrient intake, promoting glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon release, delaying gastric emptying, and inducing satiety (Nauck & Meier, 2019). However, the endogenous hormone has a short half-life of approximately 1–2 minutes due to rapid degradation by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) (Drucker, 2018).
To overcome this limitation, semaglutide was engineered as a modified GLP-1 analogue. It incorporates an amino acid substitution at position 8 to resist DPP-4 cleavage and a C18 fatty diacid side chain that facilitates strong albumin binding, thereby extending its half-life to approximately 165 hours (7 days) and enabling once-weekly dosing (Marso et al., 2016; Lau et al., 2015). These modifications provide improved pharmacokinetics compared to earlier GLP-1 RAs such as exenatide and liraglutide.
Semaglutide was first approved in 2017 under the trade name Ozempic for glycemic control in adults with T2DM. Subsequently, a higher-dose formulation was approved as Wegovy in 2021 for chronic weight management in individuals with obesity or overweight with comorbidities (Wilding et al., 2021). The efficacy of semaglutide has been demonstrated in large clinical trial programs. The SUSTAIN trials confirmed its superiority in lowering glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and reducing body weight compared to placebo and other antidiabetic agents (Marso et al., 2016). The STEP program further established its role as a potent anti-obesity agent, showing clinically meaningful and sustained weight loss of up to 15% in non-diabetic individuals with obesity (Wilding et al., 2021).
Beyond glycemic control and weight reduction, semaglutide also confers cardiovascular protection. The SUSTAIN-6 trial demonstrated a significant reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among high-risk patients with T2DM, highlighting its cardioprotective potential (Marso et al., 2016). Additionally, semaglutide is under active investigation for broader indications, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), chronic kidney disease, and even neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, reflecting its expanding therapeutic landscape (Newsome et al., 2021; Gejl et al., 2016).
Collectively, semaglutide represents a major advancement in peptide-based therapeutics, offering a dual benefit of glycemic management and weight loss, alongside promising evidence for cardiovascular and hepatic protection. Its broad clinical utility positions it as a transformative agent in the treatment of metabolic diseases.
Semaglutide: Structure
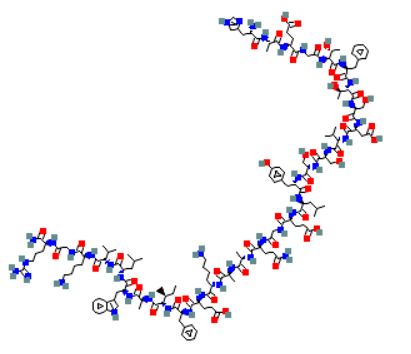
Sequence: HXEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAK-OH.steric diacid-EFIAWLVRGRG
Molecular Formula: C187H291N45O59
Molecular Weight: 4113.58 g/mol
PubChem CID: 56843331
CAS Number: 910463-68-2
Source: PubChem
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below: