MTI, Melanotan1 10mg
$44.99
Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue closely related to the naturally occurring peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, also referred to as Melanotan 2). α-MSH plays a key role in regulating skin and hair pigmentation by acting on melanocytes through strong binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). As a non-selective full agonist, α-MSH also activates melanocortin receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Melanotan 1 differs from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution and was originally developed as a sunless tanning agent. Early studies confirmed its ability to induce pigmentation but also revealed broader effects, including changes in baseline metabolism. Research on Melanotan 1 and related melanocortin-binding peptides has since provided valuable insights into the melanocortin signaling system.
$44.99
$44.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Melanotan 1 is a synthetic analogue of the endogenous peptide α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), which is sometimes referred to as Melanotan 2 in research contexts. α-MSH exerts its biological effects primarily through high-affinity binding to the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R) expressed on melanocytes, thereby regulating cutaneous and follicular pigmentation. In addition, α-MSH functions as a non-selective full agonist of melanocortin receptors MC1R, MC3R, MC4R, and MC5R, mediating diverse physiological processes beyond pigmentation. Melanotan 1 differs structurally from α-MSH by a single amino acid substitution, a modification originally designed to enhance its stability and efficacy as a pharmacological tanning agent. Initial investigations confirmed its melanogenic properties but also demonstrated effects on basal metabolic activity. Subsequent studies of Melanotan 1 and other melanocortin receptor ligands have contributed substantially to the elucidation of melanocortin signaling pathways and their roles in pigmentation, energy homeostasis, and metabolic regulation.
Melanotan 1: Structure
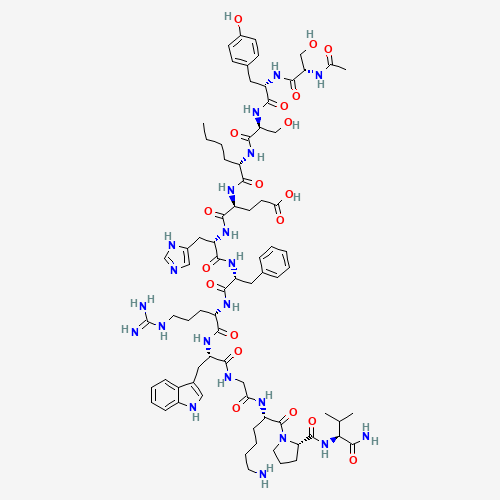
Sequence: Ser-Tyr-Ser-Nle-Glu-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val
Molecular Formula: C₇₈H₁₁₁N₂₁O₁₉
Molecular Weight: 1646.874 g/mol
PubChem CID: 16154396
CAS Number: 75921-69-6
Synonyms: Afamelanotide, Scenesse, CUV1657, MT-1
Source: PubChem
Melanotan: Research
Pharmacokinetics & Tanning Efficacy
A crossover pharmacokinetic trial in healthy male volunteers compared intravenous, oral, and subcutaneous administration of Melanotan 1 (MT-I).
Subcutaneous (SC) delivery demonstrated full bioavailability compared to intravenous dosing, while oral administration was ineffective.
The SC absorption half-life ranged from 0.07 to 0.79 hours, with a β-phase half-life of 0.8 to 1.7 hours. Clearance rates were between 0.12 and 0.19 L/kg·h; less than 3.9% of the dose was excreted in urine.
The treatment resulted in significant tanning of the forehead, arms, and neck, with effects persisting up to three weeks post-treatment. PubMed
Melanotan 1 Investigated in Fat Loss Trials
Melanotan 1 interacts with multiple melanocortin receptors, including the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Activation of MC5R has been shown to promote fatty acid oxidation within muscle tissue and shift adipocytes from fat storage toward fat utilization. Preclinical studies in mice suggest that the fat-reducing effects of melanocortin stimulation are complex, involving several receptor subtypes and physiological pathways. As a result, Melanotan 1 has attracted scientific interest for its potential role in modulating fatty acid metabolism. Beyond pigmentation, it may enhance baseline metabolic function independently of exercise an effect that could hold therapeutic value for individuals with limited ability to engage in physical activity due to severe obesity, disability, or injury.
Referenced Citations
Peripheral effect of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below: