NAD+ 750mg
$199.99
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential pyridine nucleotide and ubiquitous coenzyme present in all living cells, where it plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Acting as a redox mediator, NAD+ undergoes continuous interconversion between its oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) states, thereby facilitating electron transfer reactions fundamental to oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. Beyond its canonical role in energy metabolism, NAD+ serves as a critical co-substrate in more than 500 enzymatic reactions, underscoring its broad involvement in cellular homeostasis. Accumulating evidence suggests that maintenance of NAD+ levels contributes to enhanced skeletal muscle function, neuroprotection, and attenuation of age-associated physiological decline.
$199.99
$199.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Overview
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) represents the oxidized state of the NAD(H) redox couple and functions as a pivotal electron carrier in cellular metabolism. Its principal role lies in mediating hydride transfer during catabolic and anabolic reactions, thereby coupling redox reactions to ATP generation and other bioenergetic processes. In addition to its canonical role in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and cytosolic glycolysis, NAD+ also participates in extracellular redox signaling under specific physiological and pathological contexts.
Beyond electron transfer, NAD+ serves as a substrate for multiple classes of NAD+-consuming enzymes, including sirtuins, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), and ADP-ribosyl cyclases (e.g., CD38/CD157). These enzymes regulate a wide range of cellular processes such as post-translational protein modification, chromatin remodeling, DNA repair, calcium signaling, and transcriptional regulation. Furthermore, extracellular NAD+ has been detected as a signaling molecule released from neuronal populations within the vasculature, bladder, gastrointestinal tract, and central nervous system, implicating it in neuromodulation and intercellular communication.
NAD+ : Structure
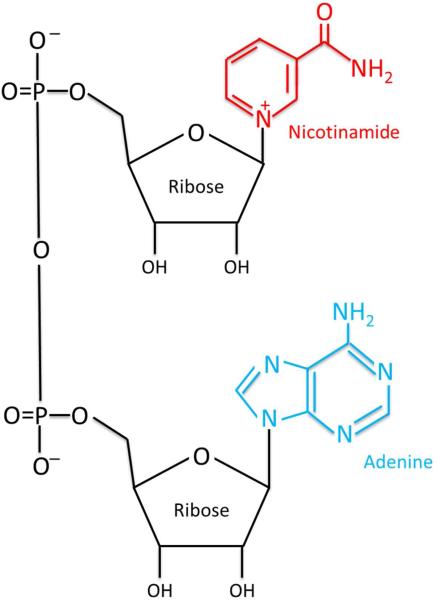
Sequence: N/A
Molecular Formula: C₂₁H₂₇N₇O₁₄P₂
Molecular Weight: 663.43 g/mol
PubChem CID: 925
CAS Number: 53-84-9
IUPAC Name: 1-[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-3-carbamoylpyridinium-5-yl dihydrogen phosphate; 5-[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl] dihydrogen phosphate
Synonyms: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, β-NAD, NAD, Endopride
Source: PubChem
NAD+ : Research
Aging & Longevity
- NAD⁺ levels decline with age in multiple tissues.
- Supplementation with precursors (e.g., NR, NMN) restores NAD⁺ and has been shown in preclinical models to improve mitochondrial function, enhance DNA repair, and extend lifespan in lower organisms.
Neurodegeneration
- Depletion of NAD⁺ is linked to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s).
- NAD⁺ boosting strategies have shown neuroprotective effects in animal models, reducing neuroinflammation and improving cognitive performance.
Metabolic Disorders
- NAD⁺ plays a crucial role in insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial biogenesis.
- Restoring NAD⁺ levels improves metabolic health in models of obesity, diabetes, and fatty liver disease.
DNA Repair & Cancer
- PARP-mediated DNA repair consumes NAD⁺.
- Cancer cells often upregulate NAD⁺ biosynthesis to sustain growth.
- Therapeutic strategies include PARP inhibitors and NAMPT inhibitors for targeting cancer metabolism.
Immune Function & Inflammation
- CD38, an NAD⁺-consuming enzyme, is upregulated in aging and chronic inflammation.
- Modulating NAD⁺ metabolism influences immune cell activation and cytokine production.
NAD+ : Scientific Journal & Authors
Shin-ichiro Imai, MD, PhD, focuses on elucidating the systemic regulation of aging and longevity in mammals, with the goal of translating these insights into effective anti-aging interventions that promote healthier and more productive later stages of life. His research highlights three key tissues as fundamental components in mammalian aging and longevity regulation: the hypothalamus (serving as the central control hub), skeletal muscle (functioning as an effector), and adipose tissue (acting as a modulator). These discoveries have been synthesized into a unifying framework referred to as NAD World 2.0 (Imai, npj Systems Biology and Applications, 2016). Through this work, Dr. Imai and colleagues aim to clarify the critical inter-tissue communications among the hypothalamus, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue in governing mammalian aging and lifespan. The ultimate objective of these studies is to develop scientifically grounded strategies for effective anti-aging interventions.
Referenced Citations
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below:




