Oxytocin 10mg
$54.99
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone with key physiological roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, maternal-infant bonding during lactation, and tissue repair. Beyond these established functions, emerging evidence indicates that oxytocin may enhance cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and mitigate complications associated with diabetes.
$54.99
$54.99
Peptide Capsules
Purchase Peptides
Purchase Blends
Overview
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide synthesized primarily in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. It is best known for its role in reproduction, where it stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and facilitates milk ejection during breastfeeding. Beyond reproductive functions, oxytocin is critical for social bonding, maternal behavior, and attachment, often referred to as the “bonding hormone”.
Recent research has expanded its relevance to broader physiological and clinical contexts. Oxytocin has been implicated in tissue repair and wound healing, as well as in metabolic regulation, with evidence suggesting potential benefits for improving glucose homeostasis and counteracting diabetes-related complications. Moreover, oxytocin signaling has been linked to enhanced cognitive function, reduced stress responses, and cardioprotective effects through modulation of vascular tone and inflammation.
Collectively, oxytocin is now recognized not only as a reproductive hormone but also as a multifaceted regulator of physical, emotional, and metabolic health, making it a target of interest for therapeutic applications in neuropsychiatric, cardiovascular, and metabolic disorders.
OXYTOCIN : Structure
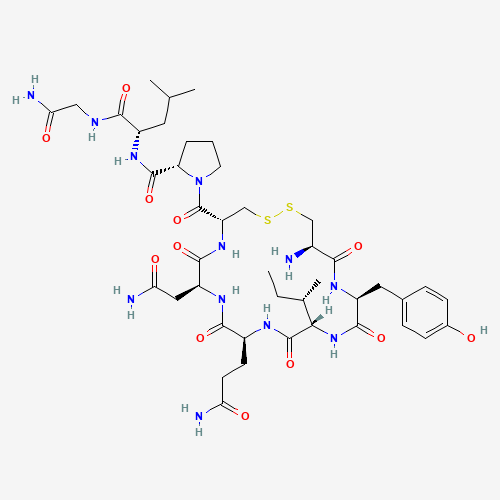
Sequence: Cys(1)-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys(1)-Pro-Leu-Gly
Molecular Formula: C₄₃H₆₆N₁₂O₁₂S₂
Molecular Weight: 1007.193 g/mol
PubChem CID: 439302
CAS Number: 50-56-6
Synonyms: Pitocin, Endopituitrina, Ocytocin
Source: PubChem
OXYTOCIN : Research
Mental Health & Social Bonds
General well-being: Oxytocin is associated with calmness, reduced fear, increased trust, and improved social interactions. Supported by literature spanning decades, this positions oxytocin as a potential contributor to mental well-being.
Aging Muscle
Recent findings indicate that oxytocin plays a key role in muscle maintenance and repair, and that age-related declines in oxytocin signaling contribute to sarcopenia (muscle wasting associated with aging). Research conducted at Berkeley revealed that as circulating oxytocin levels decrease with age, the number of oxytocin receptors on muscle stem cells also diminishes. Interestingly, administration of oxytocin can reverse this decline within days, restoring much of the muscle’s regenerative capacity.
This process is critical because muscle health depends on a balance between damage and repair. According to Elabd and colleagues, muscle repair in aged mice treated with oxytocin reached approximately 80% of the repair capacity observed in younger mice. These results suggest that oxytocin supplementation may represent a promising strategy to counteract age-related tissue degeneration and delay functional decline.
Oxytocin in Diabetes Management
Oxytocin has shown promise in enhancing metabolic regulation—particularly by improving insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake in skeletal muscle—suggesting potential utility for diabetes treatment and metabolic health improvement. Animal studies indicate that oxytocin also supports lipid metabolism, decreasing fat mass and mitigating dyslipidemia, even when food intake and activity levels are normal, emphasizing its role in energy homeostasis.
Interestingly, oxytocin’s metabolic effects appear to differ based on physiological context. In obese or metabolically compromised animal models, oxytocin administration improves glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition. However, these benefits are not observed in lean animals, indicating that oxytocin’s therapeutic potential may be confined to states characterized by metabolic dysfunction.
Further supporting translational relevance, clinical pilot studies indicate that intranasal oxytocin can reduce caloric intake in overweight individuals, even though consistent weight loss results have been uneven. One trial reported a pronounced ~9 kg weight reduction over 8 weeks, accompanied by trends toward improved postprandial glucose and insulin levels.
Cognitive Performance
Maternal deprivation at an early age is known to cause long-lasting alterations in cognitive and behavioral functioning. Research in mice suggests that these effects may be linked to oxytocin changes caused by reduced parental bonding. In one study, maternally deprived mice treated with oxytocin showed improvements in hormone levels associated with neuron development in the prefrontal cortex. Although no significant behavioral differences were observed, there was a trend suggesting that the oxytocin-treated group demonstrated better cognitive performance.
Referenced Citations
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products available on this website are intended solely for in-vitro research purposes (Latin: “in glass”), meaning they are used in experiments conducted outside a living organism. These products are not medicines or drugs, have not been evaluated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any administration to humans or animals, whether by ingestion, injection, or other means, is strictly prohibited by law.
Test
Storage Instructions:
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months.
Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you’re ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4C (39F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80C (-112F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below:




